Integrating with Salesforce using Platform Events
If you want to integrate Salesforce with multiple External Systems, and that you only want the External Systems to receive data from Salesforce. let’s say you want to notify an external system(s) whenever a record changed in salesforce. In this case, you can use callouts/outbound messaging but that will mean Salesforce takes care of every callout and callout logic. This is where you can use Platform Events. In this case, whenever there’s an update, you just Publish an Event and then Subscribers(external system) keep on listening to the Salesforce Event bus.
You can also use Platform Events when you want an External System notifies Salesforce, where the External System Publish the change on the Salesforce Event Bus and then Salesforce listens to those Events and salesforce can perform actions using the platform event trigger as required whenever get the notification.
Platform Event:
The Salesforce enterprise messaging platform offers the benefits of event-driven software architecture. Platform events are the event messages that your apps send and receive. They simplify the process of communicating changes and responding to them without requiring you to write complex logic. Publishers and subscribers communicate with each other through platform events. One or more subscribers can listen to the same event and carry out actions.
Publishing Platform Event:
- Using APEX you can Publish Platform Events.
- Publish Events using Declarative tools (Process Builder/flow).
- Publish Events Messaging using Salesforce API from an external app.
Subscription of Platform Event:
- Apex trigger on the event object to subscribe to incoming events.
- Lightning component apps and Visualforce can receive events through CometD.
- In an external app, you can subscribe to events using CometD as well.
Replay Option(ReplayID) for Event Retention:
Each event record contains a system field, called ReplayID, that the system populates after the event is published.
 |
| PE Setup |
Usage: Catch up on missed events after a certain event message, for example, after a connection failure. To subscribe with a specific replay ID, save the replay ID of the event message after which you want to retrieve stored events. Then use this replay ID when you re-subscribe.
ReplayID refers to the position of the event in the event stream. Replay ID values are not guaranteed to be contiguous for consecutive events(-2 option to receive events from the beginning and –1 option to receive new events). You can retrieve stored event messages as long as they are within the retention window of 72 hours.
 |
Publish Events using Salesforce API from an external app(External App to Platform app)
External apps use an API to publish platform event messages. You can publish events by creating records of your event in the same way that you insert sobjects. You can use Salesforce APIs to create platform event records.
External apps use an API to publish platform event messages. You can publish events by creating records of your event in the same way that you insert sobjects. You can use Salesforce APIs to create platform event records.
Usecase: Let’s say someone wants to return purchased merchandise to a vendor. An external system sends merchandise return requests to Salesforce for processing. The external system publishes a platform event to alert Salesforce to the merchandise return. An event listener (a trigger) in Salesforce receives the event and performs some actions. For example, the trigger might alert the sales representative to the return, and send a confirmation email to the customer.
Subscribe events from an external app (Platform to an external app)
External apps subscribe to platform events with CometD and perform long polling. CometD is a scalable HTTP-based event routing bus that uses an AJAX push technology
Salesforce provides a Java library, EMP Connector, which implements all the details of connecting to CometD and listening on a channel. You can use EMP Connector to subscribe easily to platform events.
External apps subscribe to platform events with CometD and perform long polling. CometD is a scalable HTTP-based event routing bus that uses an AJAX push technology
Salesforce provides a Java library, EMP Connector, which implements all the details of connecting to CometD and listening on a channel. You can use EMP Connector to subscribe easily to platform events.
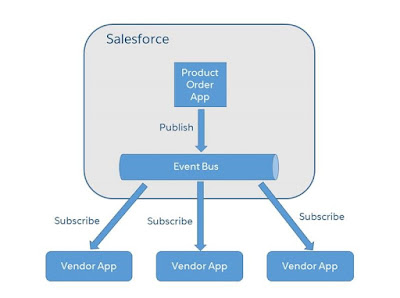
Usecase: When an opportunity closes in Salesforce, your company has won a deal with a customer. Let’s say you use vendors to ship products associated with an opportunity. Each vendor has an external app that processes shipment orders. The external app listens to platform events. When an opportunity closes, a trigger, which is part of a product order app in Salesforce, fires and publishes a platform event message. Each vendor app is notified of the event and creates a shipment order for a specific product.
Key points to remember when you considering the platform event for your integration:
- PE is designed for Pub/Sub integration model
- PE is not supported to transfer a lot of data(The maximum event message size that you can publish is 1 MB).
- You can use PE when you only want to “notify” the external system(s) with an event or message with minimal information for them to act upon.

No comments:
Post a Comment